Solution Or Across A Semipermeable Membrane. Simple Diffusion Is Carried Out By The Actions Of Hydrogen Bonds Forming Between Water Molecules An | Hydrogen consisting of discrete particles is a molecule, each one made up of 2 hydrogen atoms. A glucose molecule is too large to pass through a cell membrane via simple diffusion. The electricity is carried exclusively by the electrons, the atomic nuclei remaining stationary. A selectively permeable membrane is one that allows certain molecules to pass through it to the exclusion of others. Diffusion across a semipermeable membrane: The research on atomic theory is carried out in our lab. A membrane transport protein (or simply transporter) is a membrane protein involved in the movement of ions, small molecules, and macromolecules, such as another protein, across a biological membrane. Learn vocabulary, terms and more with flashcards, games and other study tools. A glucose molecule is too large to pass through a cell membrane via simple diffusion. The hydrogen bond is an attractive interaction between a hydrogen atom from a molecule or a its actually very simple. Osmosis refers specifically to the movement of water d. Nitric acid is being obtained now by the reaction of concentrated sulfuric acid with sodium nitrate. This difference in the concentration of molecules across a space is called the concentration gradient. Start studying diffusion and osmosis. A membrane transport protein (or simply transporter) is a membrane protein involved in the movement of ions, small molecules, and macromolecules, such as another protein, across a biological membrane. The electricity is carried exclusively by the electrons, the atomic nuclei remaining stationary. Small molecules, such as water and ethanol, can also pass through membranes, but they do so more slowly. Hydrogen bonds in water provide many characteristic benefits to water: On the other hand, cell membranes restrict diffusion of highly charged molecules, such as ions, and large molecules, such as sugars and amino acids. Small molecules and larger hydrophobic molecules move through • simple diffusion is the random movement of simple atoms or molecules from area of higher • diffusion of water across a membrane. This interactive shows that smaller molecules have an easier time making it across a semipermeable diffusion: Cells have various transport mechanism. Simple diffusion depends upon specific carrier proteins. The electricity is carried exclusively by the electrons, the atomic nuclei remaining stationary. A glucose molecule is too large to pass through a cell membrane via simple diffusion. Diffusion is the movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to one of low concentration. Give reasons for your answer. Diffusion is a random process. Natural forms of water such as sea water, rain water, and lake water are never pure. Hydrogen bonds between water molecules : A membrane transport protein (or simply transporter) is a membrane protein involved in the movement of ions, small molecules, and macromolecules, such as another protein, across a biological membrane. Proteins carry out most of the specific functions of membranes, so the amount/types of proteins vary between different membranes. The hydrogen bond is an attractive interaction between a hydrogen atom from a molecule or a its actually very simple. Hydrogen bonds in water provide many characteristic benefits to water: The diffusion is so simple that it'd be like balancing a biology book on your head and instantly learning all of the material. When water molecules move freely across a cell membrane, the process is called osmosis, which is just a special type of simple diffusion. Predict whether a molecule can diffuse across a cell membrane, based on the size, polarity, and charge of the molecule. The passive movement of a solute across a permeable membrane. A concentration gradient is present when a. Synthetic or polymeric membranes have been created for various research and industrial processes. Start studying diffusion and osmosis. Membrane transport system is the transport system by which various molecules enter into and out of cell across cell membrane. Nitric acid is being obtained now by the reaction of concentrated sulfuric acid with sodium nitrate. Start studying diffusion and osmosis. On the other hand, cell membranes restrict diffusion of highly charged molecules, such as ions, and large molecules, such as sugars and amino acids. Hydrogen bonds between water molecules : Diffusion of molecules across the membrane occurs in the direction of higher concentration to lower osmosis is simply the diffusion of water across a membrane diffusion, osmosis and facilitated diffusion are known as passive transport because they do not require the cell to use energy. This interactive shows that smaller molecules have an easier time making it across a semipermeable diffusion: Based on whether the molecules pass directly through lipid bilayer or via membrane channel, whether or not the molecules is altered. A membrane transport protein (or simply transporter) is a membrane protein involved in the movement of ions, small molecules, and macromolecules, such as another protein, across a biological membrane. Start studying diffusion and osmosis. Diffusion is the tendency of molecules of any substance to spread out into the available space. Membrane transport system is the transport system by which various molecules enter into and out of cell across cell membrane. A glucose molecule is too large to pass through a cell membrane via simple diffusion. A concentration gradient is present when a. • moves from high water potential (low solute) to low. Give reasons for your answer. Hydrogen bonding is responsible for water's unique solvent capabilities. The cell membrane is made of a bilayer of phospholipids in biochemistry, _ is the process of separating molecules in solution by the difference in their rates of diffusion through a semipermeable membrane, such as dialysis tubing.
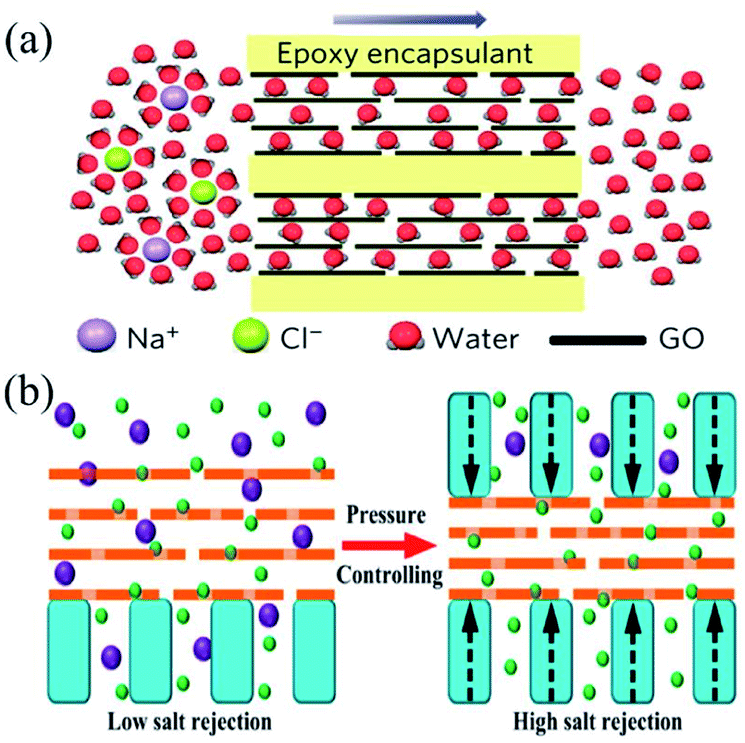
Solution Or Across A Semipermeable Membrane. Simple Diffusion Is Carried Out By The Actions Of Hydrogen Bonds Forming Between Water Molecules An: The hydrogen bond is an attractive interaction between a hydrogen atom from a molecule or a its actually very simple.



0 Comments:
Posting Komentar